Electric vehicles have changed how we refuel. Instead of quick stops at the gas station, most of us now plug in at home — sounds simple enough, right? Well, not quite. Not every charger delivers power the same way.
The difference lies in the two main types of home charging — Level 1 and Level 2.
So, what‘s the difference between level 1 and level 2 ev chargers, and which one suits your routine better? Let’s find out…

1. At a Glance
Let’s first take a quick overview. If you want to dive deeper, keep reading till the end.
| Feature | Level 1 Charger | Level 2 Charger |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 120 V (standard household outlet) | 240 V (dedicated circuit) |
| Power Output | 1–1.9 kW | 7–19 kW |
| Charging Speed | ~2–5 miles of range per hour | ~20–40 miles of range per hour |
| Time to Fully Charge (60 kWh EV) | Around 30 hours | Around 8 hours |
| Installation | None — plug into existing outlet | Requires professional installation |
| Cost | Minimal or none | $500–$1,000 (varies by setup) |
| Ideal For | Plug-in hybrids, short daily drives | Full EVs, frequent drivers |
| Extra Features | Basic charging only | Smart features (Wi-Fi, scheduling, load management) |
| Convenience | Simple but slow | Fast, efficient, and future-proof |
2. What Does ‘Charging Level’ Actually Mean?
In the simplest terms, “charging level” refers to how much electrical power flows from the outlet to your car’s battery. Each level — Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 — represents a jump in voltage and charging speed.
The concept doesn’t change, but the intensity does — the higher the voltage, the faster the energy transfer.
Level 1 and Level 2 use alternating current (AC), which your vehicle’s onboard charger converts into direct current (DC) to store in the battery.
Level 3, often called DC fast charging, skips that internal conversion entirely — it’s mostly reserved for public stations and long-distance travel, not your garage.
When people talk about selecting between Level 1 and Level 2 chargers for home use, they’re really deciding how fast they’d like that overnight refill to happen, and how much they’re willing to invest for the convenience.
Also read: Best Portable EV Chargers For 2025
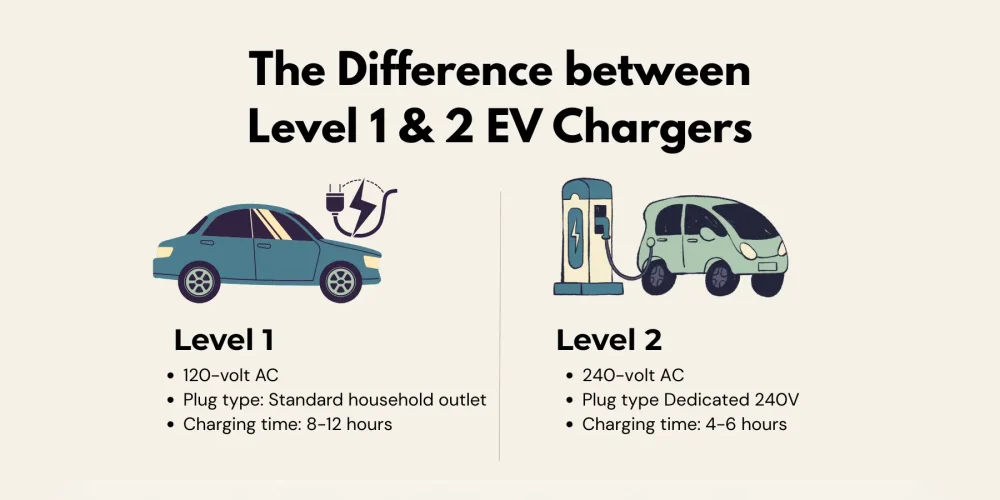
3. Level 1 vs Level 2 — Key Differences
At a glance, both Level 1 and Level 2 chargers do the same job — they feed electricity into your car’s battery. But how they do it, and how long it takes, are two entirely different stories.
The difference mainly boils down to voltage, power delivery, and convenience — three factors that can quietly transform how you live with an EV day to day.

Charging Speed
Level 1 charging operates on a standard household outlet (120 volts in the U.S.), the same one you’d use for a lamp or a coffee maker. It delivers roughly 1 to 1.9 kW of power, translating to about 2–5 miles of range per hour. It’s slow, but works well for short daily commutes or plug-in hybrids. Plug it in overnight and you’ll add around 30 to 40 miles of range.
Level 2 charging doubles the voltage to 240 V and delivers roughly 5–8 times the power output. Depending on the charger’s rating (usually 7–11.5 kW) and your car’s onboard converter, you could gain 20–40 miles of range every hour. What takes more than a full day on Level 1 might be done before lunch on Level 2.
Installation and Cost
Level 1 requires no installation — just a grounded wall outlet and patience.
Level 2, on the contrary, needs a dedicated 240 V circuit installed by an electrician. Costs vary depending on your setup, but most homeowners spend between $500 and $1,000 for parts and labor. Some states or utilities offer rebates, which helps offset the cost.
Check the U.S. Department of Energy’s website for details on tax credits.
Once installed, it’s a solid long-term setup — plug in after dinner, and by morning, you’re good to go.
Related: How Much Does It Cost To Install an EV Charger at Home?
Convenience and Smart Features

It’s not just about speed. A Level 2 unit often includes smart features (like the Duevolt Home Series) — Wi-Fi connectivity, charging schedules, energy tracking, and even integration with solar panels or time-of-use tariffs. You can set it to charge only during off-peak hours to save money over time.
Level 1 is simplicity itself — plug it in and forget about it. But that’s both its charm and its limitation. If you routinely drive long distances or forget to charge overnight, you’ll quickly find it frustrating.
Real-World Example
To put numbers into context: a 60 kWh EV (something like a mid-range crossover) would need about 30 hours on Level 1 to go from empty to full. The same car on a 11.5 kW Level 2 charger? Roughly 6 hours. That difference can mean the gap between owning an EV that fits into your life — and one that dictates it.
On the whole, Level 1 makes sense for lighter use, smaller batteries, or as a backup option. Level 2 suits daily drivers, fleets, or anyone who values time as much as range.
4. Which One is for You?
Stick with Level 1 if you drive under 30 miles a day or own a plug-in hybrid. It connects directly to a regular home outlet, so little to no setup is needed — simple, effective, and adequate for light daily use.
Go for Level 2 if you cover longer distances or simply prefer faster, smarter charging. It’s the practical choice for households with multiple vehicles or those who value efficiency and control — scheduling, energy tracking, and off-peak charging included.
Once you get used to that convenience, it’s hard to imagine going back.
Ready for an upgrade? Duevolt has you covered. We’ve got everything you need for EV charging — from Level 2 home chargers and portable units to adapters and accessories.

Our wall-mounted chargers are:
- Quick to install ✅
- Smart-ready ✅
- Compatible with both Tesla (NACS) and J1772 vehicles ✅
